Trick certbot into auto-configuring Amazon Linux 2

I use Let’s Encrypt to enable SSL/TLS encryption on all my websites. It’s brain-dead simple to configure with the EFF’s companion certbot tool and has gone a long way into the massive increase in HTTPS-by-default across the web. Unfortunately, certbot is not as familiar with the distant relative of the Red Hat family that is Amazon Linux 2.
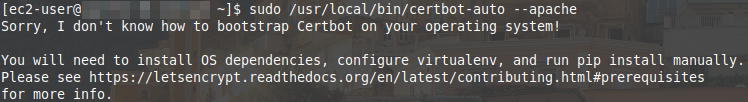
The server on which I am configuring HTTPS encryption is a new deployment so it’s pretty vanilla. My order of operations is as follows:
1) Download and put in place the certbot-auto script from the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF):
$ wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto
$ sudo mv certbot-auto /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
$ sudo chown root /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
$ sudo chmod 0755 /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
2) Enable the EPEL yum repo:
$ sudo yum install -y https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
$ sudo yum install -y epel-release
$ sudo yum-config-manager --enable epel
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo
Change both "enabled=0" to "enabled=1"
3) And now, the pièce de résistance, tricking certbot into acting just like you’re a Red Hat server:
$ sudo touch /etc/redhat-release
$ sudo /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto --apache
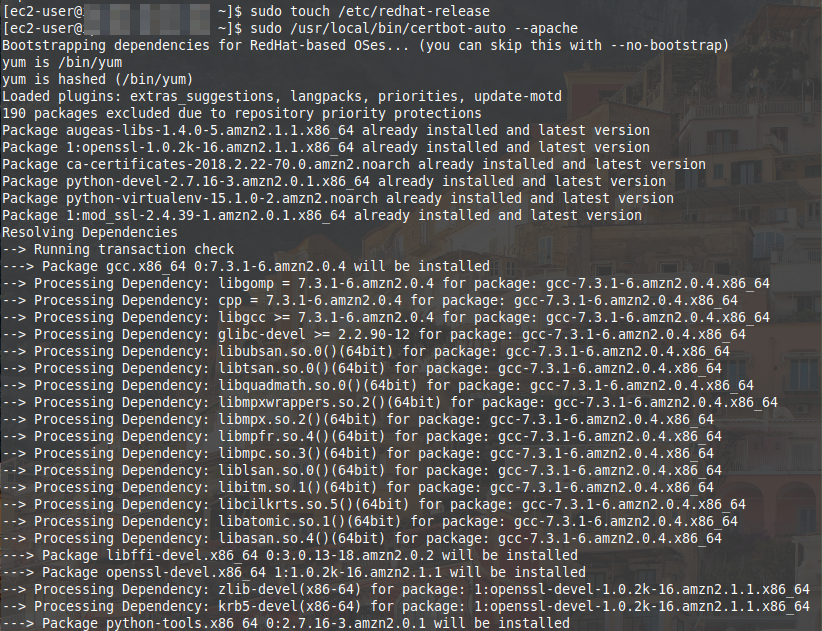
Boom. Empty /etc/redhat-release file.
If you want to DIY it or go a little off-script, these are the links I used to synthesize this information:
- Steps 1 and 2. Trouble ahead at 3: https://certbot.eff.org/lets-encrypt/pip-apache
- Post from Brad “bmw,” Warren, an EFF certbot engineer: https://community.letsencrypt.org/t/help-with-certbot-on-the-new-amazon-linux-2/49399/3
- Adding the EPEL repo: https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/ec2-enable-epel/
“To make certbot-auto try the Amazon Linux bootstrapping, you can add “Amazon Linux” to
/etc/issueor create the file/etc/redhat-release. Red Hat and Amazon Linux bootstrapping are identical.”Brad Warren, EFF Certbot Engineer
Pretty simple trick.




Leave a comment